Water Level Sensor(EF05023)
Contents
24. Water Level Sensor(EF05023)#
24.1. Introduction#
It is able to detect the water level with the on-board visible parallel wires.
24.2. Products Link#
24.3. Characteristic#
Designed in RJ11 connections, easy to plug.
24.4. Specification#
| Item | Parameter |
|---|---|
| SKU | EF05023 |
| Connection | RJ11 |
| Type of Connection | Analog output |
| Working Voltage | 3.3V |
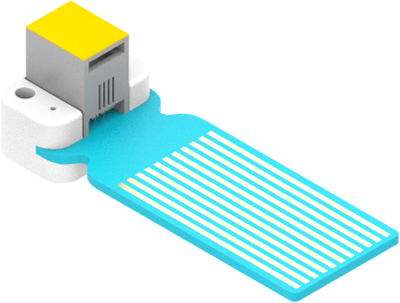
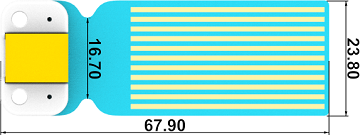
24.5. Outlook#
24.6. Quick to Start#
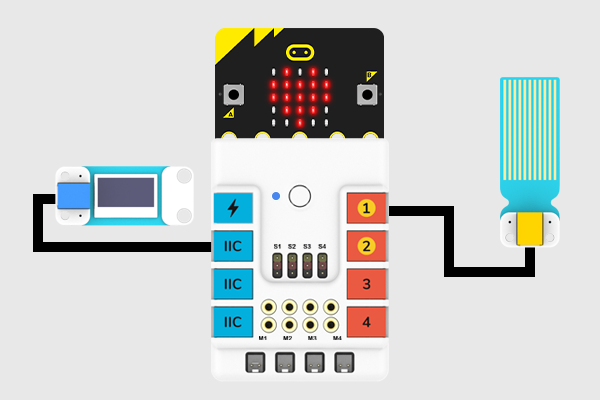
24.6.1. Materials Required and Diagram#
Connect the Water lever sensor to J1 port and the OLED to the IIC port in the Nezha expansion board as the picture shows.
24.7. MakeCode Programming#
24.7.1. Step 1#
Click “Advanced” in the MakeCode drawer to see more choices.
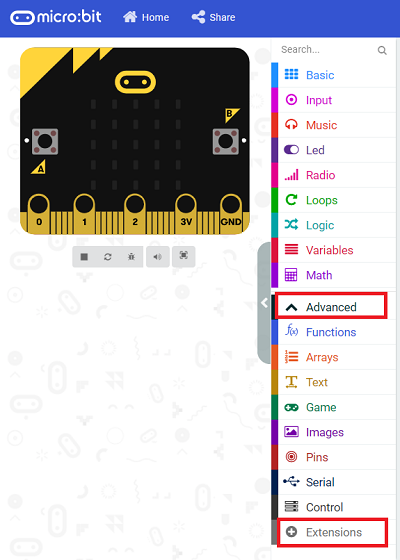
We need to add a package for programming, . Click “Extensions” in the bottom of the drawer and search with “PlanetX” in the dialogue box to download it.
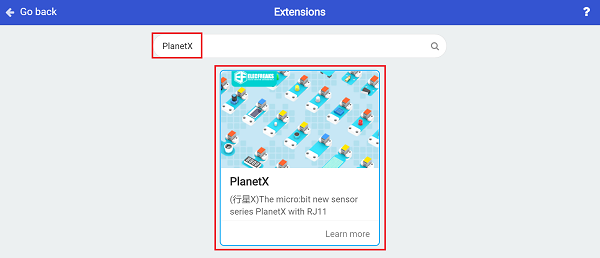
Note: If you met a tip indicating that the codebase will be deleted due to incompatibility, you may continue as the tips say or build a new project in the menu.
24.7.2. Step 2#
24.7.3. Code as below:#

24.7.4. Link#
Link: https://makecode.microbit.org/_aAJboi9L1dc9
You may also download it directly below:
24.7.5. Result#
The current value of the water level displays on the OLED screen.
24.8. Python Programming#
24.8.1. Step 1#
Download the package and unzip it: PlanetX_MicroPython
Go to Python editor
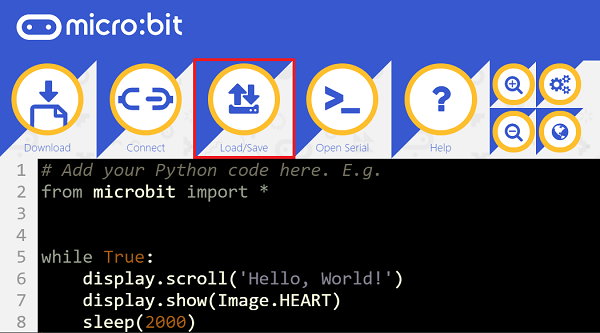
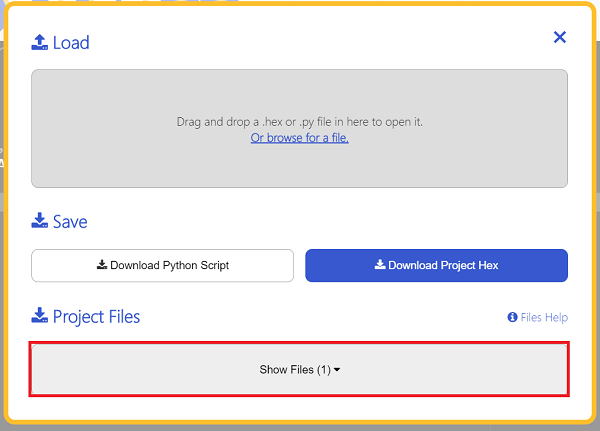
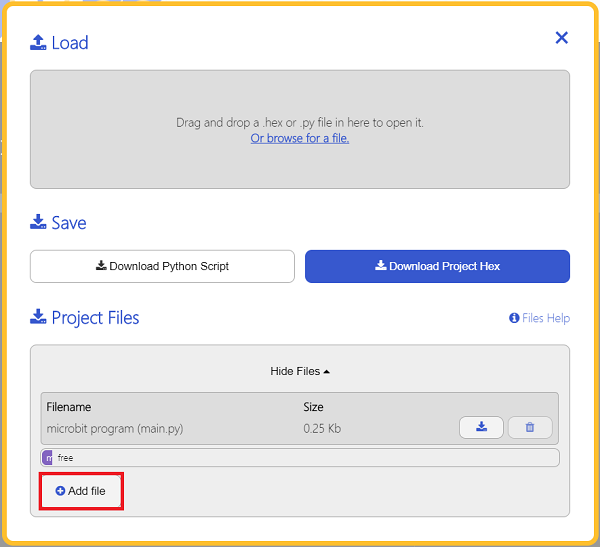
We need to add enum.py and waterlevel.py for programming. Click “Load/Save” and then click “Show Files (1)” to see more choices, click “Add file” to add enum.py and waterlevel.py from the unzipped package of PlanetX_MicroPython.
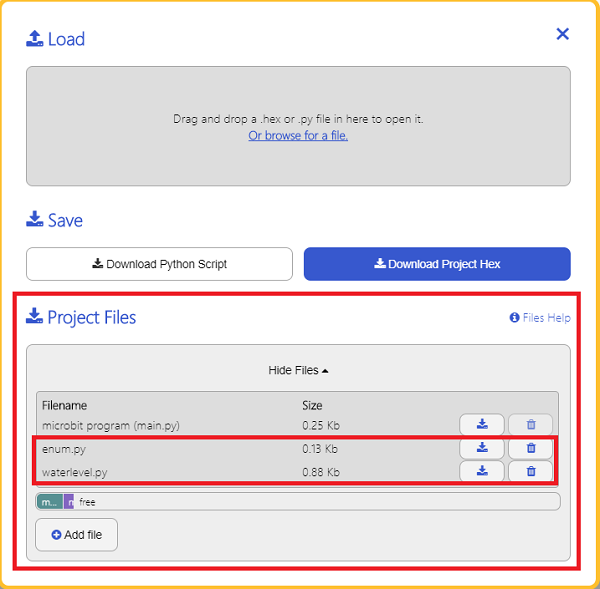
24.8.2. Step 2#
24.8.3. Reference#
from microbit import *
from enum import *
from waterlevel import *
waterlevel = WATERLEVEL(J1)
while True:
display.scroll(int(waterlevel.get_waterlevel()))
24.8.4. Result#
The current value of the water level displays on the micro:bit.
