🐰Happy Easter Day🐰Shop now with up to 30% off sitewide.
Menu


Introduction
Motor is a kind of device which can transfer electric energy into kinetic energy according to the law in electromagnetic induction. In this experiment, we are going to use a switch to control the start and stop of a motor.
Component List
Hardware:
1 x Micro:bit Board
1 x Micro-B USB Cable
1 x Microbit Breadboard Adapter
1 x Transparent Breadboard – 83 * 55 mm
1 x 5V Miniature Motors
1 x TIP 120 NPN Transistor
1 x 1N4007 Diodes
1 x 100 Ohm Resistors
1 x Breadborad jumper wire 65pcs pack
2 x Alligator Clip Wires
Tips: If you want all components above, you may need Elecfreaks Micro:bit Starter Kit.

Software:
Microsoft Makecode Online Editor
Major Component Introduction Motor
Motor is a kind of device that can transfer electric energy into kinetic energy according to the law of electromagnetic induction. Motor has a lot of categories. In our experiment, the motor we use is DC motor. When we supply DC voltage to the two terminals of motor, it will rotate. The higher the voltage, the faster it rotates.

Diodes
Diode is a kind of component with two polarities: one is for positive and the other is negative. It allows current move from the positive end to the negative end only. We can regard it as an electronic check valve. For common diode, we can judge from the color of tube for its polarity. The terminal with white color is negative polar.

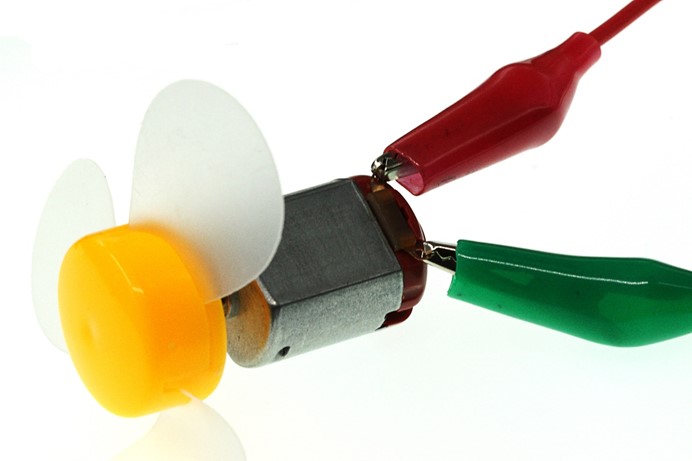
Alligator Clip Wires
Similar to the usage of jumper cable, alligator clip wire is used when some components are not suitable to use jumper cable for connection.

In this experiment, we use alligator clip wire to connect our motor.
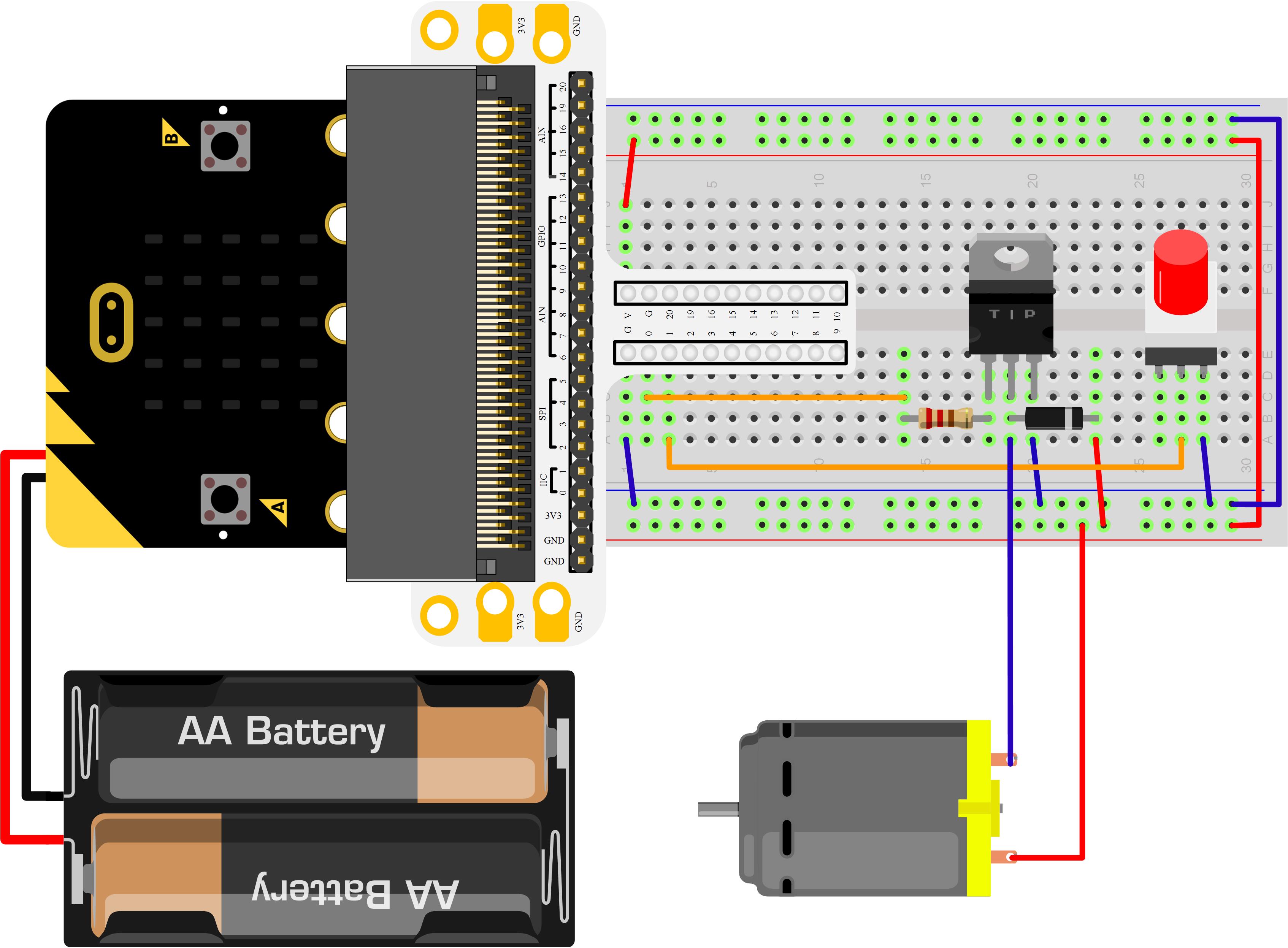
Hardware Connection
Please complete hardware connection according to the picture below.
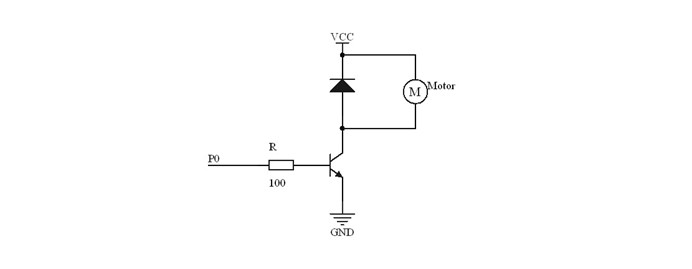
The drive current on Micro:bit IO port is too feeble to connect motor directly. At this time, we have to use a triode to amplify the current of IO port. The circuit diagram of using triode to amplify current on IO port is very similar to the circuit diagram of our last chapter “Micro:bit Experiment 09:Buzzer —— Elecfreaks Mirco: bit Starter Kit Course“. The only difference is the motor has two diodes on its both terminals. And the diode in this circuit is called Freewheel Diode. Within the motor, there has a coil. When current flow through the coil, it will produce induced electromotive force on the both terminals. When current disappeared, the induced electromotive force will generate backward voltage to the components in the circuit. It might damage these components. Freewheel diode connects the two terminals of the coil in anti-parallel. When we cut off the power supply of the inductance coil, the induced electromotive force will not disappear immediately. And the residual force will release by diode. This is a typical design of protection. Below is the partial circuit diagram of the usage of triode in amplifying the IO port current.
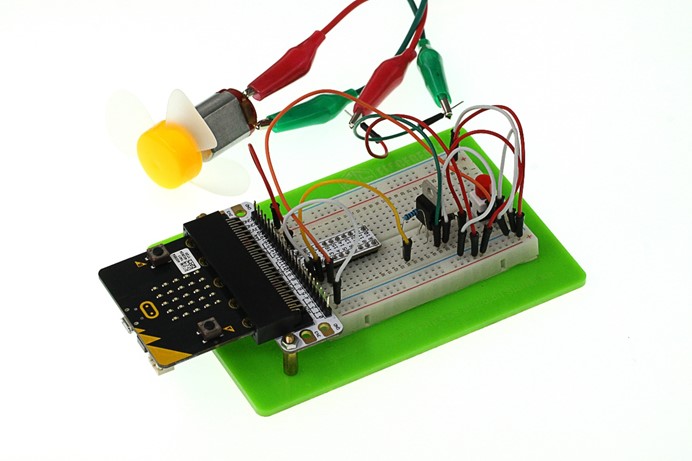
After connection, you will see:
Programming
Please open Microsoft Makecode, write your code in the edit area. I would like to suggest you program by yourself first. Of course, you can see the whole program in the link below. Just click “Edit” on the top right corner of the interface to edit your program, then click “Download” to download your code into Micro:bit.
Code Explanation
In software aspect, this experiment do not have new knowledge points. The thing we have to pay special attention to is P1 port connect button. Under brick “on start”, we have to set P1 to be up mode, or it can not recognize button signal properly.

Experiment Result
Press down the button, the motor starts rotate. Press again, it will stop move. Attention: The voltage of micro:bit power source is low. It is 3V only. Press down the button, the motor may not start. If this happened, please stir the fan blade of the motor so that it can move properly. 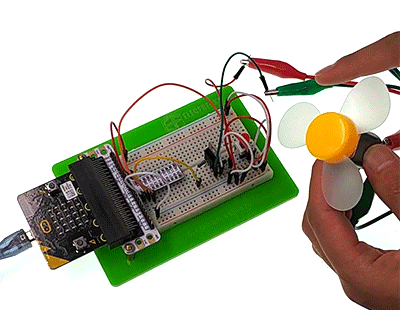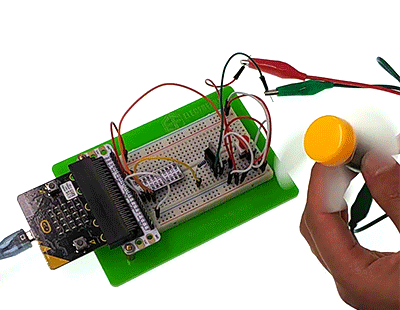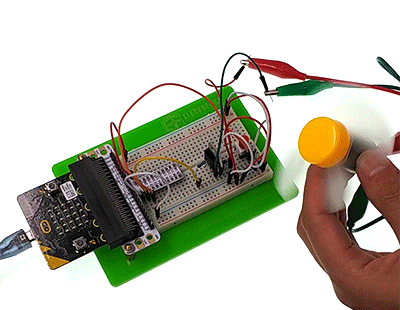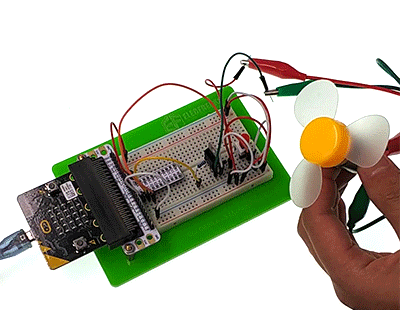
Question
If we want to use potentiometer to control the motor speed, then how to design circuit and program? We look forward to your comments and further discussions with us.
Relative Readings Start Your Micro:bit Programming Trip Micro:bit Experiment 01: LED Scroller —— Elecfreaks Micro:bit Starter Kit Course Micro:bit Experiment 02: Button —— Elecfreaks Mirco:bit Starter Kit Course Micro:bit Experiment 03: Trimpot —— Elecfreaks Mirco:bit Starter Kit Course Micro:bit Experiment 04: Photocell —— Elecfreaks Mirco:bit Starter Kit Course Micro:bit Experiment 05: RGB LED —— Elecfreaks Mirco:bit Starter Kit Course Micro:bit Experiment 06: Self-lock Switch —— Elecfreaks Mirco:bit Starter Kit Course Micro:bit Experiment 07:Temperature Sensor —— Elecfreaks Mirco: bit Starter Kit Course Micro:bit Experiment 08:Servo —— Elecfreaks Mirco: bit Starter Kit Course Micro:bit Experiment 09:Buzzer —— Elecfreaks Mirco: bit Starter Kit Course
Stay up-to-date with our latest promotions,discounts,sales,and special offers.